
When you enter a website name (domain name) in your browser, it doesn’t go there right away. First, your browser requests that a Domain Name System (DNS) server find the matching IP address. Without this step, your device won’t know where to go.
But sometimes, the DNS server doesn’t respond. Instead of loading the page, your browser displays a DNS Server Not Responding error. This means it couldn’t connect to the server that helps find websites.
The problem might be on your computer, your network, or the DNS server itself. It can happen on both Windows and macOS, and while it’s frustrating, it’s also fixable. This guide explains 10 different ways to resolve this problem on Windows and get back online.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- The error means your browser can’t reach the DNS server to load websites.
- Try another browser and switch networks to rule out simple issues.
- Disable unused network connections to avoid conflicts.
- Restart or reset your router to refresh the connection.
- Flush the DNS cache and renew your IP to clear old settings.
- Switch to a public DNS like Google or Cloudflare for better reliability.
- Turn off IPv6 if your network doesn’t fully support it.
- Use Safe Mode to check if third-party apps are causing problems.
- Temporarily disable antivirus, firewall, VPN, or proxy settings.
- Update your network adapter driver to fix connection bugs.
- If all methods fail, contact your Internet service provider (ISP) or hosting provider with the error details.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Introduction to DNS Server Not Responding Error
To understand this error, it’s important to know what DNS does. DNS stands for Domain Name System. It works in the background every time you visit a website. Its job is to turn easy-to-remember names, such as hosted.com, into IP addresses, which are sets of numbers that computers use to find each other online.
When everything works correctly, your browser sends a request to a DNS server, which replies with the correct IP address. Then, your device connects to the website.
But if the DNS server doesn’t reply or something blocks the request, your browser won’t know where to go. That’s when you see the DNS Server Not Responding error.
This error tells you that your computer or device was unable to communicate with the DNS server. The server may be down, your internet settings might be incorrect, or an issue on your system could be preventing the connection. Whatever the reason, your browser cannot load the page until the problem is sorted.
Common Causes of DNS Issues
There are a few reasons why you might see the DNS server isn’t responding error. Most of them relate to your internet connection, your device settings, or even the software you’re using.
Sometimes, it’s a hardware issue. Your router or modem might stop working properly or need a quick restart. If they’re not sending out the right signals, your device won’t be able to connect to the DNS server.
Another common cause is wrong network settings. If your computer has an old DNS address saved or your cache is full of outdated data, it can confuse your browser and stop it from reaching the correct location.
This error can also happen if your internet provider’s DNS servers are down or overloaded. In that case, your device will try to connect but won’t get any response.
Lastly, software like antivirus programs, firewalls, or VPNs can block DNS traffic in error. They’re meant to keep you safe, but sometimes they stop your browser from connecting to DNS servers.
These problems may sound technical, but many of them are simple to fix. In the next section, we show you clear steps to solve them one by one.
How to Resolve DNS Server Not Responding Error
In this section, we’ll discuss 10 easy ways to sort the DNS Server Not Responding error. Let’s start with the easy ones first.
Try a Different Browser
The first thing you should try is opening the same website in a different browser. For example, if you’re using Google Chrome and the error appears, switch to Firefox, Edge, or Safari. If the site works in another browser, the issue may be with your original browser, not the DNS.
In many cases, browsers store old or broken data that gets in the way. This is called cache. Emptying your browser cache can sort out loading issues.
You should also ensure your browser is updated. An outdated version may not work well with new internet settings. If switching browsers solves the problem, you’ll know where to focus next. If not, don’t worry, there are more steps you can try. Let’s keep going.
Troubleshoot Network Connections
If switching browsers didn’t help, the next step is to check your internet connection. Sometimes the problem isn’t with your browser or device, but rather with how you’re connected to the internet.
Start by switching your network. If you’re using Wi‑Fi, try connecting through a wired cable if possible. If you’re on mobile data, switch to Wi‑Fi. This helps you find whether the network itself is causing the DNS Server Not Responding problem.
You can also run a quick network troubleshooter. On the Windows operating system, go to Control Panel → Network and Internet → Network and Sharing Center. Under the Change your networking settings section, click Troubleshoot problems.
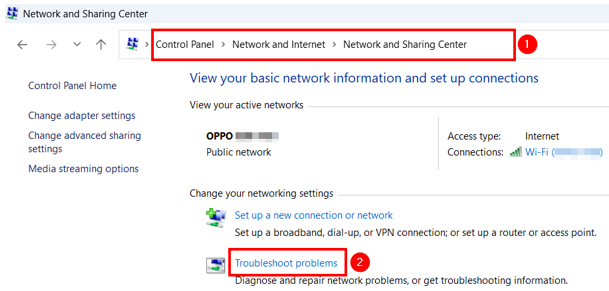
Next, click Other troubleshooters.
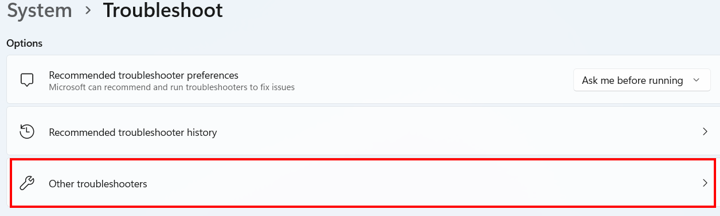
Locate Network and Internet and click Run next to it.

Your computer will scan for issues and suggest possible fixes. However, if there’s no issue, it will display a message saying You’re connected to the internet. We didn’t find any problems with your network.

These tools are built into your system and are easy to use. They often catch simple connection issues that block access to DNS servers. If everything appears to be fine here but the DNS error persists, proceed to the next method.
Disable Unused Network Connections
Sometimes, your computer has more than one network connection active at the same time. This can confuse your system and cause DNS server unavailable problems. For example, you may be connected to Wi‑Fi, but a VPN or an old Ethernet setting is still active in the background.
To do this on Windows, open Control Panel, then navigate to Network and Internet, and select Network and Sharing Center. Click Change adapter settings from the sidebar.

Here, you’ll see a list of all network connections. Right-click any connection you’re not using, such as an old VPN or Ethernet, and select Disable.

Keep only the connection you need active to help your device focus on the correct path to reach DNS servers. Once you’ve disabled the extras, revisit a website to see if the issue is gone.
Restart or Reset Router/Modem
If you’re still receiving the DNS Server Not Responding error, your router or modem may be the reason. These devices manage your internet connection, and sometimes they need a quick refresh to work properly again.
To do this, unplug your router and modem from the power outlet. Wait for almost 30 seconds, then plug them back in. Give them a minute to restart. This simple step clears out temporary issues and often brings your connection back to normal.
If that doesn’t help, you can try resetting the router. Most routers have a small reset button. Pressing and holding it (usually for 10-15 seconds) will restore the device to its factory settings.
Be careful, however, as this will erase any custom settings, including your Wi-Fi name and password. If you’ve changed something before, ensure you back it up or write it down before resetting.
Once your router is back online, check if the error has disappeared. Restarting or resetting often resolves DNS connection problems, particularly if the router has been running continuously without interruption.
Hosted®’s Web Hosting combines fast performance and strong security measures to keep your website safe and responsive.
Plus, our expert support team is available whenever you need help or guidance.
Disable IPv6
Your internet connection uses an Internet Protocol (IP) address to find and reach websites. Right now, there are 2 types:
- IPv4
- IPv6
IPv4 is the older version and is still used by most networks. IPv6 is newer and was made to handle more devices, but every router, DNS server, or website doesn’t always support it.
Sometimes, using IPv6 can lead to DNS Server Not Responding errors if your system tries to connect through it, but the network doesn’t handle it well. In these cases, switch IPv6 off and use only IPv4 to fix the issue.
Here’s how you can do this on Windows:
Press Windows + R, type ncpa.cpl, and click Enter.
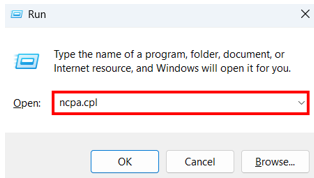
Right-click your active connection and choose Properties. In the list, find Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6) and uncheck the box. Click OK to save the change.

Once disabled, try reloading a website. If IPv6 was the cause, you should now be able to connect without the DNS error.
Restart in Safe Mode
If your website still can’t reach DNS server, it’s time to check if another program is causing the DNS problem. Some third-party apps, such as security software, VPNs, or even browser extensions, can interfere with how your device connects to the internet. The best way to test this is by restarting your computer/PC in Safe Mode with Networking.
Safe Mode starts your system with only the basic programs it needs to run. If the DNS Server Not Responding issue disappears in this mode, it means something you installed is likely causing the problem.
Here’s how Windows users can restart in safe mode:
Press and hold the Shift key on your keyboard and click Restart from the Start menu. Then, click Troubleshoot.

Click Advanced options.

Click Startup Settings.

Now, click Restart.

When your computer reboots, press the F5 key to Enable Safe Mode with Networking. Alternatively, you can also use the number keys.

Once you’re in Safe Mode, try opening a website. If it loads without the DNS Server Not Responding error, the problem is likely caused by a background app or setting.
You can then exit Safe Mode and begin turning off or uninstalling apps one at a time until you find the one that caused the conflict.
Disable Firewall & Antivirus
Firewalls and antivirus programs are designed to keep your device safe, but sometimes they block things they shouldn’t. In some cases, they may prevent your browser or system from connecting to DNS servers, and cause the DNS Server Not Responding error.
To check if this is the issue, try temporarily disabling your firewall and antivirus software. After disabling these tools, try loading a website. If it works, your security software may be blocking DNS traffic. Just remember, don’t leave your firewall or antivirus off for too long. Turn them back on once you’ve finished testing or after making changes that fix the DNS server unavailable issue.
TIP: If you’re using a proxy server or virtual private network (VPN), try turning them off to see if it resolves the DNS issue.
Update Network Adapter Driver (Windows)
If you’re using Windows, an outdated or faulty network adapter driver can cause DNS Server Not Responding errors. The network adapter is the part of your computer that connects it to the internet. That’s why keeping your driver updated helps your system talk to networks correctly.
If that doesn’t help, try uninstalling the driver. Right-click the same adapter and choose Uninstall device, restart your computer. Windows will automatically reinstall the correct driver.
Once it’s updated or reinstalled, test your internet connection again. This step should fix it, if a bad driver caused the DNS issue.
Flush DNS Cache & Renew IP Address
If previous solutions didn’t work in your case, your DNS data may be the culprit. Sometimes, your computer stores outdated or incorrect DNS data, which can cause connection errors. This is called the DNS cache.
Flushing this DNS cache removes the outdated records and forces your system to fetch fresh information. It’s also a good idea to renew your IP address in case the current one isn’t working correctly.
Here’s how to do it:
Press Windows + R, type cmd, and click Enter to open the Command Prompt. Type the following commands one by one and press Enter after each:
ipconfig /flushdns
ipconfig /release
ipconfig /renew
ipconfig /registerdnsThese commands will clear the DNS cache, release your current IP, find a new one from your network, and update your DNS records.
After completing these steps, try opening a website again. If the DNS cache or IP address was causing the problem, it should now be resolved.
Change DNS Servers
If your current DNS server isn’t working, you can switch to a public one. Popular options are:
EXAMPLE:
Google DNS (8.8.8.8, 8.8.4.4).
Cloudflare DNS (1.1.1.1, 1.0.0.1)These are fast, safe, and often more reliable. However, before switching your DNS settings, ensure you note down your current DNS addresses or configurations. Save this information in a safe place, such as on paper, so you can return to the original settings, if necessary.
You can also change DNS settings directly on your router. This will apply the new DNS servers to every device connected to your network. Log in to your router’s admin page (usually by typing its IP address into a web browser), find the DNS settings under network or WAN setup, and enter your new DNS values.
After changing DNS servers, it may take some time to take effect due to DNS propagation. Once done, try opening a website again. If DNS issues were causing the problem, switching servers should fix it.
When to Contact Your Internet Provider or Host
If you’ve tried all the fixes and still see the DNS Server Not Responding error, it’s time to reach out for assistance. The problem may be with your internet service provider (ISP) or web hosting company, rather than your device.
Before contacting support, gather some details to help them understand the issue. Write down the exact error message you’re seeing. Make a quick list of the steps you’ve already attempted, for instance:
- Changing DNS servers.
- Restarting your router.
- Flushing the DNS cache.
If you know how to access basic network logs or screenshots, those can also be helpful. The more data you give, the faster they can figure out what’s wrong and get you back online.
Sometimes, the issue is part of a bigger outage or something that only your provider can fix. So, if nothing else works, don’t wait. Reach out and let them take a look.
![Get fast, secure Web Hosting with expert support from Hosted® Strip Banner Text - Get fast, secure Web Hosting with expert support from Hosted®. [More Info]](https://www.hosted.com/articles/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/dns-server-not-responding-2-1024x229.webp)
FAQS
What’s the difference between a DNS server and a web server?
A DNS server helps your browser find the correct IP address by translating domain names into numbers. A web server stores the actual website content and delivers it to your browser when requested. If the DNS server fails, your browser won’t even reach the web server, which is why DNS issues must be fixed first.
How do I know if the issue is with my device or my ISP?
If the DNS Server Not Responding error appears on all your devices, the issue may be with your ISP or router. If the issue only occurs on one device, then the problem is likely specific to that system.
Will changing DNS settings affect all devices on my network?
Changing DNS settings on your router will affect every device connected to your network, since the router shares those settings with all users. However, if you change the DNS settings only on your computer, phone, or tablet, then the change applies to that device alone. This is helpful if you’re just testing or troubleshooting the error on one device without affecting others.
Is it safe to use free public DNS servers?
Generally, yes. Reputable public DNS servers (e.g., Google and Cloudflare) are safe and offer strong performance. They often have extra security features, including blocking harmful websites. However, avoid unknown DNS services, as some may log your activity or redirect traffic. Always stick with trusted providers for safety and speed.
Can I use multiple DNS servers at the same time?
Yes, most systems allow you to set a primary and a secondary DNS server. If the primary one fails, your device will try the secondary. This adds a layer of backup and can help avoid downtime. Just ensure both servers are reliable and fast to ensure smooth internet browsing.
Other Related Tutorials
– How To Configure WordPress DNS Settings
– How To Fix DNS_PROBE_FINISHED_NXDOMAIN Error
– How To Fix DNS_PROBE_STARTED Error
– How to Fix: This Site Can’t Provide a Secure Connection Error
– How to fix ERR_ADDRESS_UNREACHABLE in Google Chrome

















