Sometimes, when you try to open a website in Google Chrome, you may see an error message that says NET::ERR_Certificate_Transparency_Required. This message means that Chrome couldn’t verify the site’s Secure Socket Layer (SSL) certificate, thus it blocks the page to protect your information.
An SSL certificate is a digital file that proves a website is secure. It keeps your data safe when you browse, fill out forms, or make payments online. Chrome checks these certificates to ensure the site is listed in the Certificate Transparency (CT) log. If it’s not, this error shows up.
This tutorial shows you what this error is and why it occurs. Then, we explain how to fix this problem. Whether you’re the website owner or just someone trying to visit a page, there are clear steps to help you solve it. Lastly, we’ll see how to avoid the certificate transparency required error.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- The NET::ERR_Certificate_Transparency_Required error happens in Chrome when an SSL certificate is not listed in Certificate Transparency logs.
- Certificate Transparency helps Chrome check if a website’s SSL certificate is valid and trusted.
- Website visitors can try simple fixes like updating Chrome, clearing the cache, disabling extensions, or checking antivirus settings.
- Website owners should reissue their SSL certificate with proper CT logging or reinstall it correctly on the server.
- Using tools like the Hosted® cPanel makes it easy to install custom SSL certificates that meet Chrome’s CT rules.
- Enterprise users can change the Chrome policies to bypass CT checks for trusted internal domains.
- Bypassing the error is risky for regular users and should only be done if you completely trust the website.
- Keeping browsers updated and using valid, trusted SSL certificates helps avoid this error in the future.
- Always test your website in multiple browsers after installing or updating an SSL certificate.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Introduction to the NET::ERR_Certificate_Transparency_Required Error
The ERR_Certificate_Transparency_Required error is a specific SSL-related error that appears in Google Chrome when the browser cannot verify the authenticity of an SSL/TLS certificate due to missing or incomplete Certificate Transparency (CT) information.
This means that the certificate is either not logged properly in public CT logs or was issued by a Certificate Authority (CA) that failed to meet Google Chrome’s CT requirements. When this happens, Chrome blocks access to the website and displays the error to the user as a security warning.
Now, you may be wondering what Certificate Transparency (CT) is. It’s a security standard and open framework, designed to detect mis-issued or rogue SSL/TLS certificates by requiring Certificate Authorities to log all issued certificates in publicly auditable CT logs. These logs are append-only, cryptographically verified records of certificates.
The purpose of Certificate Transparency is to:
- Prevent CAs from issuing certificates without proper domain owner approval.
- Detect and respond to fraudulent or unauthorized certificate issuance.
- Allow domain owners and browsers to monitor SSL certificate issuance in near real-time.
Each issued SSL certificate must be accompanied by Signed Certificate Timestamps (SCTs), and proof that the certificate has been submitted to one or more CT logs. SCTs can be delivered in 3 ways:
- Embedded in the certificate during issuance.
- Served via the Transport Layer Security (TLS) handshake using the Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) stapling.
- Delivered via a TLS extension during the handshake.
Based on an announcement and details from the Chrome Certificate Transparency GitHub page, Google made CT logging mandatory for all publicly trusted SSL certificates in Chrome 68 after April 2018.
If a certificate is missing the required SCTs, or the SCTs point to logs that Chrome no longer trusts, the browser will throw the NET::ERR_Certificate_Transparency_Required error.
This enforcement helps Chrome:
- Ensure that only publicly logged certificates are trusted.
- Protect users from malicious or misconfigured websites.
- Strengthen the overall security of the HTTPS system.
This policy applies to Extended Validation (EV), Organization Validated (OV), and Domain Validated (DV) certificates alike. If these certificates lack valid CT log entries, Chrome will consider them untrustworthy, even if they’re valid and correctly installed.
In short, this error is a strict security measure that prevents users from accessing potentially unsafe sites with improperly logged SSL certificates.
Common Causes of Error
The key reasons why the NET::ERR_Certificate_Transparency_Required error may appear in Google Chrome are linked to how the SSL certificate is set up or handled by the browser and system.
Missing Certificate Transparency Log Entry:
The most common cause is that the website’s SSL certificate was not properly logged in a Certificate Transparency (CT) log. Every SSL certificate issued through a trusted Certificate Authority must be added to these public logs.
If this step is skipped (for example, the certificate isn’t added to the transparency log due to a mistake by the issuer or a request from the site owner) or something goes wrong during the process, Chrome will block access and show the NET::ERR_Certificate_Transparency_Required error. It does this to protect users from fake or misused certificates.
Misconfigured SSL Certificate:
Another reason could be a misconfigured SSL certificate. This may mean the certificate is self-signed (created by the website instead of a trusted Certificate Authority), expired or installed incorrectly. Chrome checks certificates closely, and even small issues can trigger this error.
Outdated or Unsupported Browser:
If you’re using an old version of Google Chrome, it may not be able to read modern SSL certificates correctly. Chrome must be updated to understand and verify Signed Certificate Timestamps (SCTs) linked with Certificate Transparency. An outdated browser can lead to false errors, even when the certificate is valid.
Interference from Antivirus or Firewall:
Sometimes your antivirus or firewall software can interfere with Chrome’s connection checks. These programs may try to scan secure websites and accidentally block or change how the certificate is read. This can confuse Chrome, making it think the certificate is unsafe, even when it’s not.
All these causes are linked in one way or another to how certificates are handled. Let’s see how you can resolve this error as a website owner and visitor.
Solutions for Website Visitors
If you see the NET::ERR_Certificate_Transparency_Required while trying to access a website, the problem may not always be on your side. But before assuming it’s a website problem, try a few things to see if the error disappears:
- Disable Firewall and Antivirus Temporarily
- Update Google Chrome Browser
- Clear Browser Cache and Cookies
- Disable Chrome Extensions
- Chrome Clear SSL State
If any of the above methods don’t work in your case, and if you trust the website you’re trying to access, you can bypass the Certificate Transparency warning. This tells Chrome to ignore the issue and let you access the site.
However, this method isn’t recommended because it can expose your device to harmful content, and it’s important to undo the change once you’re done visiting the site to avoid security risks on other websites.
To bypass the warning, open Chrome and type chrome://flags in the address bar.
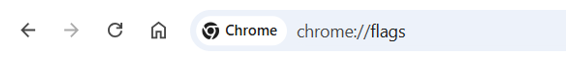
Then, use the search bar to find the setting called Insecure origins treated as secure.
Once found, choose Enabled from the dropdown list next to it. After that, click Relaunch to restart Chrome and apply the change.
If the issue continues, contact the website owner. The error could be caused by a problem with their SSL certificate which they should fix. To do so, look for a contact form or email address on the site. If you can’t find one, try reaching out through their social media profiles.
Solutions for Website Owners
If you’re the website owner facing the certificate transparency required error, your SSL certificate is missing required Certificate Transparency (CT) data. To resolve this, try the following fixes:
Protect your website and its visitors by securing sensitive information with a Domain Validated SSL Certificate.
Trust and security are vital for any online business, so safeguard your site with an SSL certificate that’s both quick and easy to implement.
Reissue & Reinstall the SSL Certificate
First, contact your Certificate Authority (CA), the company you got the SSL certificate from. Tell them you’re getting a CT-related error in Google Chrome.
It’s possible they forgot to add it to the Certificate Transparency log, which can trigger the error. You can ask them to resolve the issue by updating the log. You’ll usually find a support email or a ticket system on the website where you got the certificate. If your SSL certificate comes with your WordPress Hosting plan, contact your hosting provider for help.
If this doesn’t help, you may ask them to reissue the certificate with proper Signed Certificate Timestamps (SCTs) included. These SCTs prove that the certificate is logged in public CT logs.
In many cases, the CA will ask you to generate a new Certificate Signing Request (CSR). A CSR is a file that contains your domain details and public key. You can create it using your hosting control panel or server tools like OpenSSL.

Once you receive the new SSL certificate from the CA, reinstall it on your web server. Ensure you upload all certificate files correctly, including the root and intermediate certificates.
For instance, if you’re a Hosted® user, go through the following steps:
Type your domain.tld/cpanel in the browser’s address bar and click Enter. Ensure you replace domain.tld with your domain name. You’ll see the below screen. Fill in your username and password and click Log in.
Next, head to Security → SSL/TLS.
Click Manage SSL sites.

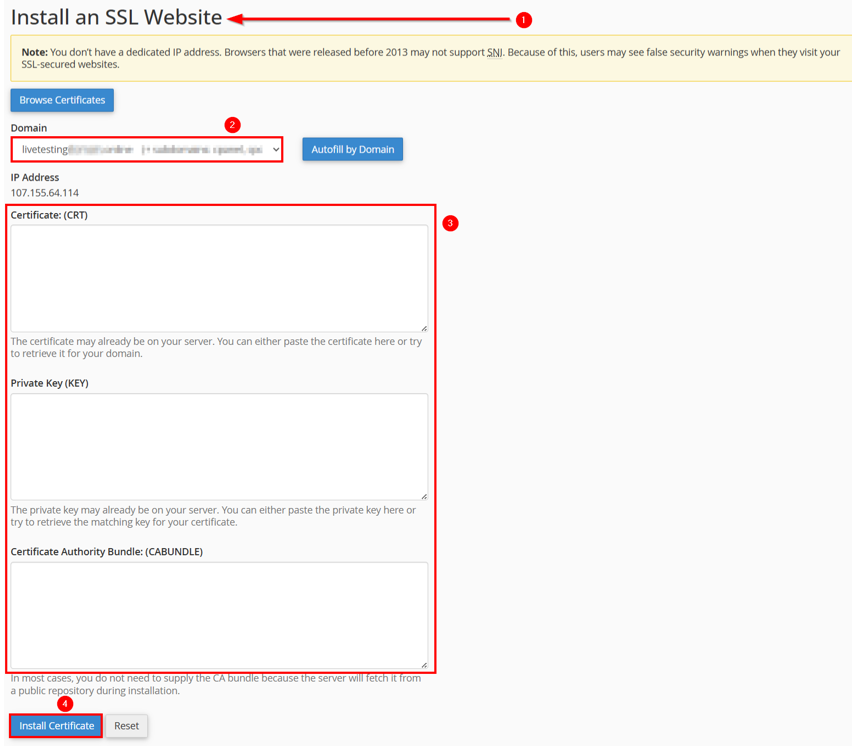
Navigate to Install an SSL Website. Choose your domain name and enter the contents of your SSL certificate file (which may end in .cert, .cer, or .crt) and private key (with a .key extension) file.
Remember, in many situations, you don’t need to manually provide the Certificate Authority Bundle: (CABUNDLE), as the server typically retrieves it from a public source during installation.
Once added, click Install Certificate to complete the process.
After installation, clear your browser cache and test the site in Chrome. If everything is correct, the error should disappear, and your site will load securely again.
Set Chrome Policy to Disable Certificate Transparency Enforcement
If you previously chose not to include your SSL certificate in the Certificate Transparency logs for privacy reasons, apply the Certificate Transparency exemption policy.
This ensures users can still access your site without running into errors. This method is only recommended for system administrators who wish to temporarily bypass the Certificate Transparency (CT) check for trusted internal domains.
Consider that this exemption method only works on Chrome browsers managed by an organization. It’s intended for schools, businesses, or other groups that control user access and browser settings across devices.
By applying this policy, you can prevent Chrome from requiring Certificate Transparency for your domain or subdomain. As a result, visitors within your organization won’t see the NET::ERR_Certificate_Transparency_Required error.
We recommend using these steps when setting up policies in Chrome Enterprise. On Windows systems, the policy may appear in this format:
For Exact Domain:
SoftwarePoliciesGoogleChromeCertificateTransparencyEnforcementDisabledForUrls1 = yourdomain.com
For Domain + All Subdomains:
SoftwarePoliciesGoogleChromeCertificateTransparencyEnforcementDisabledForUrls2 = .yourdomain.com
Once you’ve added the domain, apply the changes and restart Chrome. You can also confirm the policy has been applied by visiting chrome://policy/ in the address bar and looking for CertificateTransparencyEnforcementDisabledForURLs.

After restarting, Chrome will skip the CT check for the following, and the error should no longer appear:
1. https://yourdomain.com
2. https://sub.yourdomain.com
3. https://*.yourdomain.comRemember, this method does not fix the SSL certificate itself. It only bypasses the check on the browser side, and it’s not meant for public-facing websites.
Note: This bypass does not make a certificate valid. It only tells Chrome to ignore the CT requirement for specific domains. Use this only in trusted internal networks. Do not apply it to public or production domains without strong justification. Disabling CT enforcement weakens security. Therefore, this setting should be managed centrally in enterprise environments and monitored regularly for compliance.
How to Prevent NET::ERR_Certificate_Transparency_Required
To avoid the NET::ERR_Certificate_Transparency_Required error later, it’s important to follow a few smart steps when setting up or renewing your SSL certificate.
First, always get your SSL certificate from a trusted Certificate Authority (CA). Web browsers approve these companies and follow strict rules. Using a trusted CA ensures your certificate is safe, valid, and supported by Chrome and other browsers.
Next, ensure your certificate is Certificate Transparency (CT) compliant. When you order a certificate, ask your provider to include Signed Certificate Timestamps (SCTs). These SCTs prove that the certificate was added to public CT logs. Most trusted CAs do this automatically, but it’s good to double-check before installing the certificate.
Lastly, use SSL monitoring tools to monitor your certificate’s status. These tools can alert you if your certificate is missing from the CT log or if something goes wrong. This way, you can fix issues before users ever see an error. If you follow these steps, you can help keep your website safe, trusted, and error-free.
![Secure your website with a Domain Validated SSL Certificate Strip Banner Text - Secure your website with a Domain Validated SSL Certificate. [Get started]](https://www.hosted.com/articles/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/Tut-OS-131-2-1024x229.webp)
FAQS
Can I skip this error and still visit the site?
You can, but it’s not recommended. Chrome lets you click Advanced and then Proceed to [website] to visit the page. However, this may expose your data to risks, so only do this if you completely trust the site and understand the dangers.
How can I check if my SSL certificate includes SCTs?
You can check for SCTs by inspecting your site’s SSL certificate in Chrome. Click the padlock icon in the address bar, select Connection is secure, then Certificate is valid. In the certificate details, look for a section called Signed Certificate Timestamp List. You may also use online tools like SSL Labs to see if SCTs are present. If SCTs are missing, it means the certificate was not logged properly in the CT logs.
Can a free SSL certificate cause the NET::ERR_Certificate_Transparency_Required error?
Yes, a free SSL certificate can trigger this error if it’s not issued with valid Signed Certificate Timestamps (SCTs) or misconfigured. Free and paid certificates must meet Chrome’s CT logging rules. Contact your certificate provider if you’re unsure.
Is it safe to ignore the NET::ERR_Certificate_Transparency_Required error?
Don’t ignore this error unless you are sure the website is safe, and you trust the source. The error means Chrome cannot confirm the certificate’s validity through public transparency logs. Ignoring it may expose you to fake websites or security threats. It’s best to contact the site owner or return later once the issue is fixed. You can bypass the error but only when you understand the potential risks.
What is a Signed Certificate Timestamp (SCT)?
An SCT proves that an SSL certificate has been submitted to a public Certificate Transparency log. Chrome looks for SCTs during the HTTPS handshake. If SCTs are missing or invalid, Chrome blocks the connection and shows the NET::ERR_Certificate_Transparency_Required error to keep users safe.
Why is Certificate Transparency important for website security?
Certificate Transparency adds a strong layer of protection by making all issued SSL certificates publicly visible. It prevents Certificate Authorities from secretly or accidentally issuing certificates for your domain to hackers or attackers. When Chrome enforces CT, it ensures only verified and publicly logged certificates are trusted. This helps catch fake or unauthorized certificates early, protects users from phishing sites, and keeps the web more secure. Without CT, users and site owners are more exposed to invisible certificate misuse.
Do all browsers check for Certificate Transparency?
No, not all browsers enforce Certificate Transparency (CT) as Chrome does. While Google Chrome strictly checks for CT logs and SCTs, other browsers like Firefox or Safari may not fully enforce these checks. This is why the error may only appear in Chrome. Even if another browser doesn’t show the error, the certificate could still be misconfigured. Website owners should fix the issue properly rather than rely on browser differences to mask the problem.
How long does it take to fix this error?
For website owners, fixing the error may take a few hours. It involves contacting the Certificate Authority, reissuing the certificate with CT support, and reinstalling it on the server. For visitors, clearing the cache or updating Chrome can be done in minutes if the issue is on their side.
Do I need to switch hosting providers to fix this error?
Not usually. This issue is related to the SSL certificate, not the hosting itself. You can stay with your current host and fix it by installing a properly logged certificate. However, if your host doesn’t support custom SSL installations, you may want to upgrade or switch plans.
Will Google penalize my site in search rankings due to this error?
While the error does not directly affect your SEO rankings, it can hurt user trust and engagement, which influences your site’s performance. If users can’t access your site because of SSL errors, bounce rates can increase, and trust can decrease. Also, Google favors secure websites (HTTPS) in search results. So, if your certificate is broken or incomplete, it’s best to fix it quickly to protect your visitors and your site’s reputation in search engines.
Other Related Tutorials
– How To Fix ERR_SSL_VERSION_INTERFERENCE Error
– How To Fix SSL_ERROR_RX_RECORD_TOO_LONG Error
– How To Fix SSL Handshake Failed Error
– How To Fix ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR
– How To Fix ERR_BAD_SSL_CLIENT_AUTH_CERT Error

















